Expenditure Categories:
An expenditure category describes the source of your organization’s costs. For
example, an expenditure category with a name such as Labor refers to the cost
of labor. An expenditure category with a name such as Supplier refers to the
cost incurred on supplier invoices.
In addition, you can use expenditure categories in your AutoAccounting rules
and in your reporting. Expenditure categories are used for grouping expenditure
types for costing.
Defining Expenditure Categories
N èSetup è
ExpendituresèExpenditure Categories
To Define expenditure categories:
In
the Expenditure Categories window, enter a unique name for the expenditure
category and enter its description and also the Effective Dates.
Save
your work.
Some
of the Examples of commonly Used Expenditure Categories
Expenditure Category Name
|
Description
|
Labor
|
Labor
costs
|
Travel
|
Travel
expenditures
|
In-House
Recoverable
|
Use
of corporate assets
|
Outside
Services
|
Outside
services
|
Material
|
Materials
|
Other
Expenses
|
Expenses,
excluding travel
|
Units
N èSetup è SystemsèUnits
N èSetup è SystemsèUnits
A
unit of measure records quantities or amounts of an expenditure item. You
assign a unit to each expenditure type. Oracle Projects predefines the units
Currency and Hours.
To
define a unit of measure:
1. Navigate
to the Unit Lookups window.
2.
Enter Type as UNIT, Meaning as UNIT, Application-Projects, and Description as
UNIT.
3.
Enter the following information-Code, Meaning, Description, Tag Value (optional
–– tag value is not used by Oracle Projects), Effective dates & Enabled
Checkbox checked.
Save
your work.
Define Expenditure Types
An expenditure type is a classification of cost
that you assign to each expenditure item you enter in Oracle Projects.
N èSetup è
ExpendituresèExpenditure Types
1.
Name: Enter a unique name for the expenditure type.
2.
Expenditure
Category and Revenue Category: Enter
the expenditure category and revenue category you want to associate with this
expenditure type.
3.
Unit of
Measure: Enter the unit of Measure
you want Oracle Projects to use when calculating the cost for this expenditure
type. You must enter Hours for labor expenditure types.
4.
Tax
Classification Code: This is a new
feature in R12. You need to click Tax Classification Code and select the tax
classification code for customer invoice lines for this expenditure type and
operating unit. Oracle Projects uses this code as the default tax
classification code based on the Application Tax Options hierarchy that you
define in Oracle E-Business Tax for Oracle Projects and the specified operating
unit.
5.
Rate Required: If this expenditure type requires a cost rate, check
the Rate required check box, then choose Cost Rate to navigate to the
Expenditure Cost Rates window and enter a cost rate and its effective date(s).
6.
Description
and Dates: In the Description, Dates
region, enter a description for the expenditure type. You can optionally enter
effective dates for the expenditure type.
7. Expenditure
Type Classes: In the Expenditure Type Classes region, enter the
Expenditure Type Class or classes you want Oracle Projects to associate with
This expenditure type, to determine how to process the expenditure item.
Expenditure
Type Classes
An expenditure type class tells Oracle Projects how to process an expenditure
item. Oracle Projects predefines all expenditure type classes.
Oracle
Projects uses the following expenditure type classes to process labor costs for
interfacing to Oracle General Ledger:
1.
Straight Time – Payroll straight time
2.
Overtime – Overtime premium on a project
Oracle
Projects uses the following expenditure type classes to process non–labor
project costs:
1.
Expense Reports – Oracle Projects expense reports are interfaced to
Oracle Payables for employee reimbursement.
2.
Usages – Asset usage costs are interfaced to Oracle General Ledger.
3.
Supplier Invoices – Oracle Payables supplier invoices are interfaced
from Oracle Payables to Oracle Projects.
4.
Miscellaneous Transaction – Miscellaneous Transactions are used to track
miscellaneous project costs.
5.
Inventory – This expenditure type class is used for the following
transactions:
–
Project Manufacturing transactions that are interfaced from Manufacturing or Inventory
to Oracle Projects.
-Oracle
Inventory Issues and Receipts that are interfaced from Oracle Inventory to
Oracle Projects in a manufacturing or non–manufacturing installation
For
Example: Expenditure Category is Labor; Expenditure Type is Administrative
& Expenditure Type Class is Straight Time.
Define Event Types
An implementation-defined classification of events
that determines the revenue and invoice effect of an event. Typical event types
include Milestones, Scheduled Payments, and Write-Offs.
N èSetup è Billing è Event Types
1. Enter a unique, descriptive name for this event
type.
2. Revenue Category: Enter the revenue category
that you want to associate with this event type.
3. Class: Enter a classification for this event type
Automatic. An Automatic classification generates an automatic
event for revenue or invoice amounts that
may be positive or negative, depending on your implementation of billing
extensions.
Manual. A Manual classification allows you to enter both a
revenue amount and a bill amount. These two amounts can be different. Classify
an event type as manual when you need to indicate different
revenue and bill amounts.
4. Enter the effective start and end dates.
5. Tax Classification Code. This is a new feature in
R12 .Optionally; click Tax Classification Code to select the tax classification
code for customer invoice lines created for this event type and operating unit.
Oracle Projects uses this as the default tax classification code based on the
Application Tax Options hierarchy that you define in Oracle E-Business Tax for
the Oracle Projects application and the project's operating unit. For more
information on setting up tax classification codes and the hierarchy of
application tax options, see the Oracle E-Business Tax User Guide.
Define Budget Entry Method
Budget entry methods
specify and control how you enter a budget or forecast. You use budget entry
methods when you create budgets and forecasts that use budgetary controls and
budget integration features.
N èSetup è Budgetsè Entry Methods
Oracle Projects predefines three budget entry
methods:
You can define additional budget entry methods
during implementation.
Defining Budget Entry Methods
1. Navigate
to the Budget Entry Methods window.
2. Enter a
name and description for the budget entry method.
3. Select an
entry level. The entry level can be Project, Top Tasks, Lowest Tasks, or Top
and Lowest Tasks.
4. Select
Categorized by Resources if you want to categorize amounts by resources.
5. Select a
time phased type. The choices are Date Range, GL Period, PA Period, or None.
6. Select
the enterable fields for cost and revenue using the displayed check boxes.
7. Save your
work.
Define Resource List
Define the resource list as a hierarchy of
resources up to two levels. The top level is restricted to resource types, such
as organization, expenditure category, and revenue category. Use the resource
types Event Type, Expenditure Type, Revenue Category, and Expenditure Category
to define the second level of the hierarchy:
N èSetup è Budgetsè Resource Lists
1.
Enter the Resource List name and Description.
2.
Group Resources By: Choose how you want to group the resource list. If
you choose to group the resource list, and then you enter resource groups.
Select the resource group, and override the alias and order if necessary.
3.
If the resource list is job-based, then you must enter a job group to be
used for summarization. The Resources region then displays jobs that belong to
the job group you entered.
4.
In the Resources region, enter the resources for each resource group. If
you do not use grouping for the resource list, then use the Resources region to
enter resources for the resource list.
5.
Select the resource type and resource .Resource type could be
Expenditure type, Event etc
6.
Alias and the Order number defaults automatically .Override the values
if required.
Define Rate Schedules.
Oracle Projects determines rates from a combination
of rate schedules or rate overrides and uses these rates to calculate cost,
revenue, and bill amounts. We can define four types of rate
schedules:
·
Employee
·
Job
·
Non-Labor
·
Resource Class
Define Billing and Non
Billing rate schedules
N èSetup è
ExpendituresèRate Schedules
First Define Employee Bill Rate Schedule
To define a rate schedule:
1. Specify the Operating Unit. This is a new
feature in Release 12. Specify the operating unit to which your organization
and rate schedule belong. When you have access to only one operating unit, that
operating unit appears as a default value in this field.
2. Specify the organization that maintains the
schedule.
The organization you enter can be any organization
from your organization hierarchy, regardless of whether the organization has
the Expenditure Organization classification, and regardless of the start and
end dates for the organization.
3. Enter a schedule name and a description of the
schedule.
4. Specify a currency for the schedule.
Note: You can specify a different currency for your
Bill Rate Schedule if the Enable Multi Currency Billing option is enabled for
the operating unit. See: Enable Multi Currency Billing, Billing Implementation
Options, and Oracle Projects Implementation Guide.
4. Check the Share across Operating Units check box
to allow other operating units to use this schedule.
Note: To share bill rate schedules, you must also
enable the Share Bill Rate Schedules across Operating Units options in the
Billing tab of the Implementation Options window. See: Share Bill Rate Schedule
Across Operating Units, Billing Implementation Options, and Oracle Projects
Implementation Guide.
5. Select a schedule type.
6. Rates can be
defined employee wise or Job wise. Incase of job wise rate Click on the Job Tab
and Select Job group.
7. Select Employee name against whom the rate need
to be defined.
8. Employee Number and UOM defaults.
9. Enter the Rate or Markup percent.
10. Enter the effective start and end date for the
rate.
Now, define Job Bill
Rate Schedule
Just update the
Organization, Schedule Name and Currency and save your work.
Now, define Non
Labor Bill Rate Schedule
Just update the
Organization, Schedule Name and Currency and save your work.
Define Transaction Sources
N èSetup è
ExpendituresèTransaction Sources
Transaction sources identify the source of external
transactions you import into Oracle Projects using Transaction Import The
transaction source determines how Transaction Import processes transactions.
Some transaction sources are system–defined, and you can create others to fit
your business needs. When you create a transaction source, you control the
Transaction Import processing by the options that you select.
Predefined Transaction Sources
Oracle
Projects predefines several transaction sources. The following table lists some
of the predefined transaction sources:
Transaction Source Used to Import Records From:
AP
INVOICE Oracle Payables (supplier
invoices)
WARNING:
Do not use this transaction source when you run the PRC: Transaction Import
program. It is intended only for use by the Oracle Projects processes to import
Oracle Payables invoices.
ORACLE
PAYABLES Oracle Self–Service Expense.
Oracle
Self–Service Time Oracle Self–Service
Time
Time
Management Oracle Time Management
Oracle
Time and Labor Oracle Time and Labor
Predefined
Transaction Sources for Manufacturing and Inventory Costs:
Oracle
Projects predefines three transaction sources for importing expenditures from
Oracle Manufacturing and Oracle Inventory:
Transaction
Source Used to Import:
Inventory- Manufacturing material costs Inventory
Misc
Inventory- issues and receipts
entered in the Miscellaneous Transactions window in Oracle Inventory
Work In Process- Manufacturing resource costs
Implementation
Option Set Ups
Costing Implementation Options
Navigate to the Implementation Options
Screen.
N èSetup è System è Implementation Options
1.
Operating Unit: It’s a new feature in R12. You can define your
Implementation options based on your Operating Units. It means that from a
single responsibility you can Define/Query Multiple Operating Unit based
Implementation Options Set Ups. The same feature was not available in previous
releases.
2.
Ledger: In R10.5.10 the same information was defined under
Set of Books Tab. In R12 the name has been changed to Ledger. If you are
implementing Oracle Projects for a single organization, then you must specify a
set of books to tell Oracle Projects which set of general ledger books to use.
If your implementation of Oracle Projects is for multiple organizations, Set of
Books is a display-only field. Its value defaults from the Legal Entity for the
operating unit.
3.
Summarization
Period Type: summarization period
type is used when updating project summary amounts.
4.
Calendar Name: When you implement Oracle Projects, you can select
the calendar used to maintain PA periods.
5.
PA Period
Type: Specify a Period Type, which is
used to copy Project Accounting Periods from the calendar associated with the
GL Set of Books.
6.
Maintain
Common PA and GL Periods: When this
option is enabled, the system automatically maintains PA period statuses as you
maintain the GL period statuses.
7.
Default Asset
Book: Optionally, select a
default asset book from the list of values. The value that you select for this
field will be the default value for all project assets that you create. You can
override the default value at the asset level.
8.
Default
Reporting Organization Hierarchy: You
specify an organization hierarchy and version to indicate which organization
hierarchy you want Oracle Projects to use as the default reporting organization
hierarchy.
1.
Functional
Currency: This display-only field
shows the functional currency of your company’s set of books.
2.
Exchange
Rate Date Type: Specify a default
exchange rate date type for converting foreign currency transactions from the
transaction currency to the functional and project currencies.
3.
Exchange Rate
Type: Select the GL Rate Type to
determine the rate. The system-defined rate types, such as Corporate, User, or
Spot, are defined in Oracle General Ledger.
1.
Project
Numbering: Specify whether you
want Oracle Projects to number projects automatically, or whether you plan to
enter project numbers manually.
2.
Project/Task
Owning Organization Hierarchy: You
assign a project/task owning organization hierarchy to the operating unit to
control which organizations can own projects and
tasks.
3.
Version: Enter the version number.
1.
Expenditure Cycle Start Day- You
specifies an Expenditure Cycle Start Day to indicate the day your seven–day
expenditure week begins. If you specify Monday as the expenditure cycle start
day, the week ending date on all expenditures, including timecards and expense
reports, is the following Sunday. You can choose any day of the week as your
expenditure cycle start day.
2.
Interface Cost to GL: If you want to interface costs with Oracle General
Ledger, you must enable the system options for labor and usage costs interface.
Interface
Employee Labor Cost- Enabled
Interface
Usage, Inventory, and WIP, Miscellaneous and Burden Costs-Enabled.
3.
Expenditure/Event Organization: You assign
an expenditure/event organization hierarchy to the operating unit to control
which organizations have the following capabilities:
–
incur
expenditures
–
own project
events
–
be assigned
to a resource list as a resource
4. Version:
Enter the version number.
Auto Accounting
N èSetup è Auto
AccountingèAssign Rules
Oracle Projects creates many different accounting
transactions throughout its business cycle (when posting labor cost debits and
labor revenue credits, for example). You can use AutoAccounting to specify how
to determine the correct general ledger account for each transaction.
When you implement AutoAccounting, you define the
rules and circumstances that determine which general ledger accounts Oracle
Projects uses. Oracle Projects then uses the rules when performing accounting
transactions.
Define AutoAccounting rules to generate account
combinations, and then assign a set of rules to each AutoAccounting transaction
you want to use for your company.
Costing
|
|
Expense Report Cost Account
|
Determined
cost account for expense report items.
|
Expense Report Liability Account
|
Determines
liability account for expense report costs
|
Labor Cost Account
|
Determines
cost account for all labor items, including straight time and overtime
|
Labor Cost Clearing Account
|
Determines
clearing account for labor costs
|
Supplier Invoice Cost Account
|
Determines
cost account for adjusted supplier invoice items.
|
Total Burdened Cost Credit
|
Determines
credit account for total burdened costs for all items on burdened projects
|
Total Burdened Cost Debit
|
Determines
debit account for total burdened costs for all items on burdened projects
|
Usage Cost Account
|
Determines
cost account for usage items
|
Usage Cost Clearing Account
|
Determines
clearing account for usage costs
|
Labor Cost Account Function
When you
run the PRC: Distribute Labor Costs process, Oracle Projects calculates labor
cost amounts based upon employee labor cost overrides and labor costing rules.
After calculating labor costs, Oracle Projects uses the Labor Cost Account
transactions to debit an expense account for raw labor costs.
The Labor Cost Account function consists of the
following transactions:
• Indirect Private Labor
• Indirect Public Labor
• Private Billable Labor
• Private Non–Billable Labor
• Public Billable Labor
• Public Non–Billable Labor
• All Labor
• Capital, All
• Contract, All
• Indirect, All
• Capital, Private, Capital
• Capital, Private, non–Capital
• Capital, Public, Capital
• Capital, Public, non–Capital
Dening a Lookup Set
In lookup sets you specify pairs of values. For
each intermediate value, you specify a corresponding account segment value. One
or more related pairs of intermediate values and segment values form a lookup
set. Use the Segment Value Lookup Region zone to specify an intermediate value,
and then map that intermediate value to a specific segment value of your
Accounting Flexfield.
To implement the Labor Cost Account function,
Implementation team defines three lookup sets:
• One lookup set to map organizations to companies
• One lookup set to map organizations to cost
centers
• One lookup set to map service types to each
Fremont’s six expense accounts for indirect labor
Segment Value Lookups
You
may need several lookup sets to map organizations to cost centers, expenditure
types to account codes, event types to account codes, or for other situations
where the segment value depends upon a particular predefined parameter.
You
can use a lookup set more than once; several AutoAccounting rules can use the
same lookup set.
You
define and modify lookup sets using the AutoAccounting Lookup Sets window.
AutoAccounting Lookup
Sets Window Reference
Use
this form to define, view, and maintain AutoAccounting lookup sets.
Name.
Enter a unique,
descriptive name for this lookup set.
Segment Value Lookup
Region
Use
this zone to specify an intermediate value, and then map that intermediate
value to a specific segment value of your Accounting Flexfield.
AutoAccounting
matches an intermediate value derived from an AutoAccounting rule with an
intermediate value in the lookup set and determines the corresponding segment
value you specify to derive an account code from your chart of accounts.
Intermediate
Value. Enter the
intermediate value that you want to map to an Accounting Flexfield segment
value.
Ensure
that you have entered a valid intermediate value. Valid intermediate values are
those that match intermediate values that may be derived from AutoAccounting
rules. Specify the values in the base language and ensure that the case and spelling
match exactly. (For more information about the base language, see: Multilingual
Support in Oracle Projects, Oracle Projects Fundamentals.) For example, if you
are mapping organization intermediate values to cost center segment values, you
cannot enter 'RISK ANALYSIS' for an organization with the name of 'Risk
Analysis'.
If
AutoAccounting does not find a matching intermediate value in the lookup set,
AutoAccounting provides an error message (Incomplete AutoAccounting Rules)
notifying you that it could not build an Accounting Flexfield combination. You
must correct your AutoAccounting setup and resubmit the process that triggered
the AutoAccounting error.
Selecting
an Intermediate Value Source
To define an AutoAccounting
rule, you first specify an intermediate value (an "input" for the
rule). You can draw an intermediate value from one of three intermediate value
sources:
Constant
|
Always supply a particular
intermediate value (usually an Accounting Flexfield segment code)
|
Parameter
|
Use a predefined parameter
as an intermediate value; make the rule context-sensitive based on one value
|
SQL Select Statement
|
Execute a SQL select
statement to retrieve an intermediate value; make the rule dependent on
multiple values and/or conditional statements
|
Segment
Value. Enter the
Accounting Flexfield segment value that you want to map to with this
intermediate value.
Ensure
that you have entered a valid segment value. Valid segment values are those
that are defined for your Accounting Flexfield segments. Values must match
exactly numerically.
If
AutoAccounting does not find a matching segment value in the lookup set,
AutoAccounting provides an error message (Invalid Accounting Flexfield)
notifying you that it could not build a valid Accounting Flexfield combination.
You must correct your AutoAccounting setup and resubmit the process that
triggered the AutoAccounting error.
Dening AutoAccounting Rules
AutoAccounting rule you define supplies one
Accounting Flexfield segment value at a time. Thus, you need to specify one
AutoAccounting rule for each segment in your Accounting Flexfield for each
AutoAccounting transaction you want to use. Some of the AutoAccounting rules
you define can be quite simple, such as always supplying a constant company
code or natural account. Others can draw upon context information (parameters),
such as the revenue category for a particular posting or the organization that
owns a particular asset. You can even use multiple parameters to provide a
segment value. You can reuse the same AutoAccounting rules for many different
functions and their transactions.
- One rule supplies the
appropriate value for the Company segment of Organization’s Accounting
Flexfield; Organization uses a lookup set to define this rule.
- One rule supplies the
appropriate value for the Department segment; Organization uses
a lookup set to define this rule.
- Rules supply the appropriate
account code for the Account segment; the indirect, private labor rule
uses a lookup set, and the other five use constant values.
- Rules supply the appropriate
account code for the Sub Account segment; the indirect, private labor rule
uses a lookup set, and the other five use constant values.
- Rules supply the appropriate
account code for the Product segment; the indirect, private labor rule
uses a lookup set, and the other five use constant values.
Assigning Rules to Transactions
AutoAccounting function consists of several distinct
transactions; you assign rules to each transaction you want to use. These rule
assignments then determine which general ledger account AutoAccounting uses to
process that transaction. After you enable a transaction, you match each
segment in your Accounting Flexfield with the appropriate AutoAccounting rule.
For example, if you have a two-segment Accounting Flexfield containing a
Company segment and an Account segment, you assign one rule to the Company
segment and one rule to the Account segment.
Function Transaction’s Enabled
All
Labor- All Labor Items Enabled Checkbox Ticked
Capital,
ALL – All Labor Items on Capital Projects.
In
the same manner you will need to define other Auto Accounting Rules
Non Labor Resources
You specify a name and a description of an asset,
or pool of assets, to define a non–labor resource. For example, you can define
a non–labor resource with a name such as Earth Mover to represent one earth
mover your business owns.
Every usage item you charge to a project must
specify the non–labor resource utilized and the non–labor resource organization
that owns the resource.
When defining your non–labor resources, you can
choose only expenditure types with the Usage expenditure type class.
You can use the non–labor resource organization in
your AutoAccounting rules for Usage & Miscellaneous cost and
revenue.
Defining Non-Labor Resources
N èSetup è ExpendituresèNon Labor Resource
To define non-labor resources:
1.
In
the Non-Labor Resources window enter a name, description, effective date(s),
and a usage expenditure type for each non-labor resource your organization
owns.
2.
For
each non-labor resource you define, enter the organization(s) to which the
resource is assigned in the Organizations region. Enter the effective dates
during which the resource is owned by each organization.
The
organizations you enter can include any organization from your organization
hierarchy, regardless of whether the organization has the Expenditure
Organization classification, and regardless of the start and end dates for the
organization.
3.
If
you want to override the cost rate of the expenditure type by the resource and
organization combination, choose Cost Rates and enter the cost rate for the
operating unit in question and the effective date in the Cost Rates Overrides
window.
4.
Save
your work.
Non Labor Cost Rates - Defining Cost Rates
for Expenditure Types
An expenditure type cost rate is a currency amount
that Oracle Projects multiplies by the expenditure type unit to calculate cost.
You define a cost rate in the Expenditure Types
window by selecting an expenditure type and entering a cost rate for it. You
can select only a non–labor expenditure type that requires a cost rate. You
cannot define a cost rate for a non–labor expenditure type that does not
require a cost rate. Instead, you must disable the expenditure type and create
a new one that requires a cost rate and has a unique name.
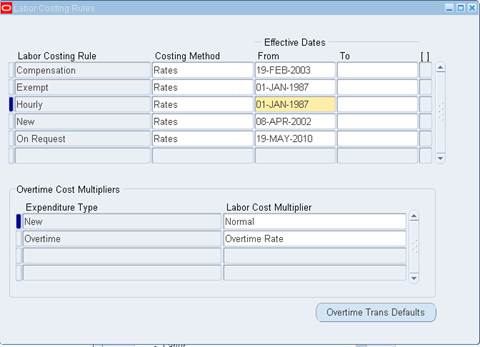
Labor Costing Rules
N èSetup è Costingè LaborèLabor Costing Rules
A labor costing rule determines how an employee is
paid. You define a labor costing rule for each pay type your business uses.
For example, you can define a labor costing rule
for pay types such as exempt, non–exempt, uncompensated, compensated, or
hourly.
When an employee charges time to a project, Oracle
Projects processes the labor hours according to the employee’s labor costing
rule.
For example, if an employee’s labor costing rule is
Hourly, the employee is eligible for overtime pay; if the employee’s labor
costing rule is Exempt, the employee is not eligible for overtime pay.
1.
In
the Labor Costing Rules window, enter a unique rule name and select a costing
method.
Costing
methods determine how labor costs are calculated. The available options are:
Rates: When you select Rates, Oracle
Projects calculates the labor costs for entered hours using hourly cost rates.
Extension: When you select Extension, labor
costs are calculated by the labor costing extension. When using this option you
are not required to maintain hourly cost rates in Oracle Projects.
2.
If
overtime hours are created by the overtime calculation extension, you can select
Overtime Trans Defaults and specify a default project and task by operating
unit for system generated expenditure items.
3.
Enter
the Effective Dates during which the labor costing rule is valid.
4.
If
your employees enter overtime hours manually, use the Overtime Cost Multipliers
region to assign cost multipliers to overtime expenditure types. When a costing
method of Rates is selected and a transaction is charged to an expenditure type
that has an assigned multiplier, the multiplier is applied as labor costs are
calculated.
Note:
If the transaction is charged to an overtime task and a cost multiplier is
assigned to the task, the task multiplier takes precedence over the expenditure
type multiplier.
If
overtime hours are derived using the overtime calculation extension, you can
use the Overtime Cost Multipliers region to default expenditure types for
system generated expenditure items.
5.
Save
your work.
Define Labor Costing Overrides
N èSetup è
CostingèLaborèLabor Costing Overrides
1. To
override labor costing:
2. In the
Labor Costing Overrides window, enter either the Employee Name or Employee
Number for the operating unit under question. Then select Find.
3. The
current overrides for the selected employee are displayed.
4. Specify
whether you wish to override the assigned rate schedule or enter an overriding
cost rate by choosing an override type:
5. Schedule:
Enter the overriding rate schedule in the Cost Rate Schedule field.
6. Rate:
Enter an overriding rate. Optionally, select a new currency code and define
currency conversion attributes.
7. Enter the
Effective Dates during which the labor costing override is valid for this
employee.
8. Save your
work.






















 Get Flower Effect
Get Flower Effect
2 comments:
thanks
Unique information that is not available on internet
Post a Comment